Guide to automate changeset releases
Published on:
read
Let’s say you have a npm package which is published to npm registry. But you don’t like the manual process of releasing it. You want an automated way which is reliable adds changelog and overall fastens the release process.
Here is a step by step guide on how to automate the release process.
What is changeset?
Before we start, let’s understand what is changeset.
Changeset↗ is a tool that helps you manage your changelog and release process.
In order to automate the Github releases and NPM package publishing, we can use GitHub Actions with Changesets Releaser Action↗.
Setting up the repository permissions
In order to automate the changeset releases, we need to setup the repository permissions which allows the GitHub Actions to create a tags, releases and pull requests.
For this step, we need to go to the repository Settings -> Actions -> General.
You will see the workflow permissions section at the bottom of the page:
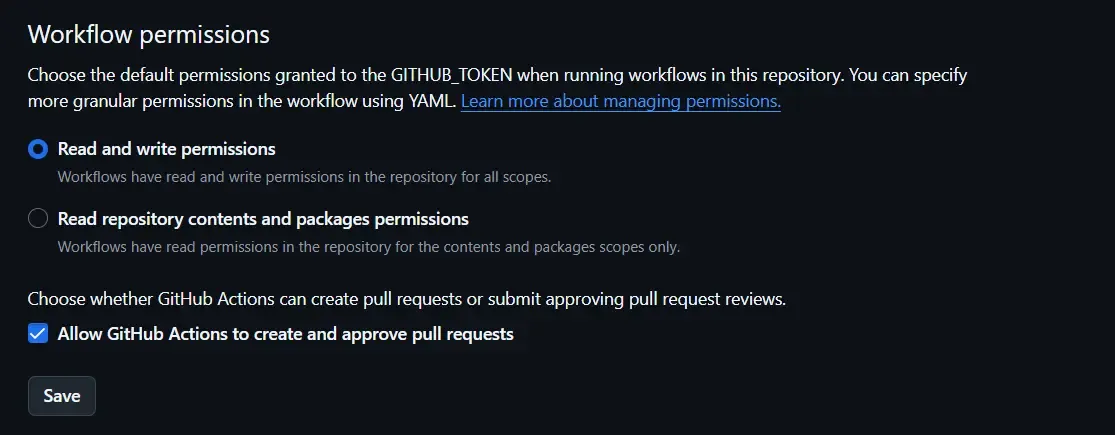
You need to enable the following permissions:
- Grant read and write permissions to GITHUB_TOKEN.
- Allow Github Actions to create and approve pull requests.
Setting up NPM access tokens
Next step is to generate an NPM access token. If you already have an automation token, skip the creation step and use it (provided that you have saved it somewhere).
Navigate to npmjs.org↗, and log in if you’re not already.
Go to Profile Picture → Access Tokens → Generate New Token → Granular Access Token.
Give it a propper name, select needed package, scopes and permissions.
Now generate it by clicking on the Generate Token button.
At this point, the token will be shown. Copy it and save it somewhere safe, because you won’t be able to see it again.
Setting up Repository Secrets and Variables
Now, we need to store this generated NPM token in our repository’s secrets and variables.
For that go back to your repository and then navigate to Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions.
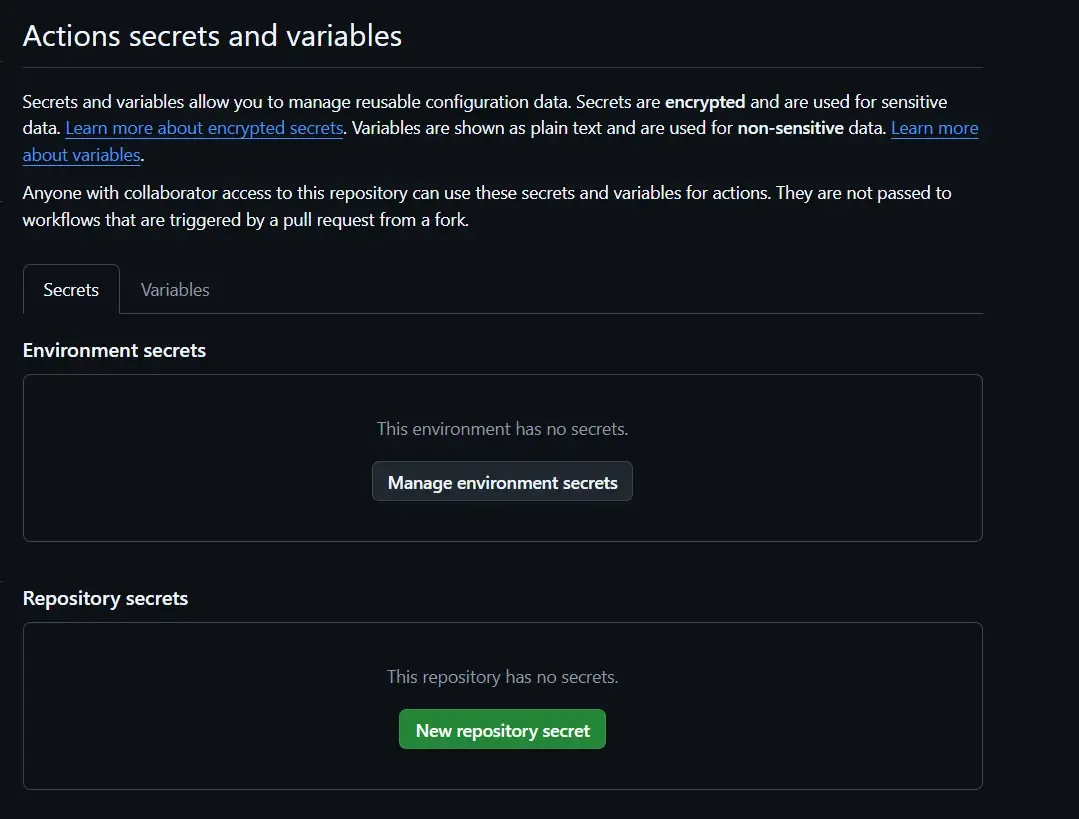
Click on the New repository secret button. You’ll be presented with the “New secret” form.
Add a new secret as NPM_ACCESS_TOKEN and the secret should be the NPM token you generated in the previous step.
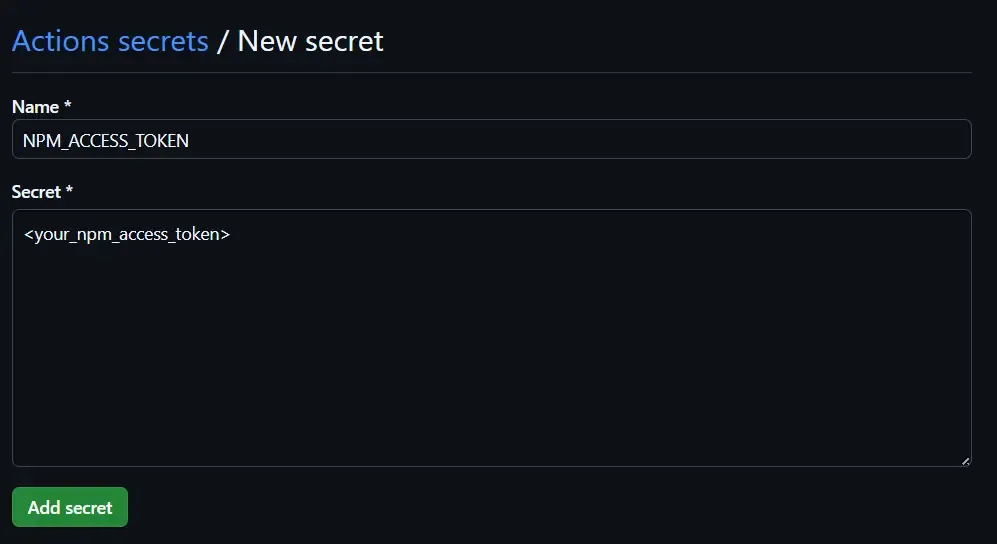
Save the secret by clicking on the Add secret button.
Setting up Changeset
Now, we need to setup the changeset in our repository.
First, we need to install the @changesets/cli and @changesets/changelog-github package.
I am using
pnpmas my package manager. If you are using different package manager, please refer to the Changeset documentation↗ for the correct installation command.
pnpm add -D @changesets/cli @changesets/changelog-githubWe need to also initialize the changeset in our repository. Run the following command:
pnpm dlx changesets initIt will create a .changeset folder in your project, containing a config.json file. This is also where your changesets will live.
Make your changeset release public by adding the following to your config.json file:
.changeset/config.json
{
"access": "public"
}Also, change the changelog field to @changesets/changelog-github and add your GitHub repository name to the repo field.
.changeset/config.json
{
"changelog": ["@changesets/changelog-github", { "repo": "your-github-username/your-repo-name" }]
}Set commit field to false as well. This will prevent changesets from committing the changes to the repository.
.changeset/config.json
{
"commit": false
}Now, we need to add the following scripts to your package.json file:
package.json
{
"scripts": {
"release:version": "changeset version",
"release:publish": "changeset publish"
}
}Setting up GitHub Actions
Now, we need to setup the GitHub Actions workflow.
Create a new file in the .github/workflows folder called release.yml.
Let’s give it a name “Release”.
.github/workflows/release.yml
name: ReleaseNext, we need to define the event that will trigger the workflow. In this case, we want to trigger the workflow when a push is made to the main branch.
.github/workflows/release.yml
on:
push:
branches:
- mainAlso, we will define the concurrency. This will prevent previous runs if a new one is triggered.
.github/workflows/release.yml
# cancel previous runs if a new one is triggered
concurrency:
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.event.number || github.ref }}
cancel-in-progress: trueNow, let’s first define create_pr job which will create a pull request.
.github/workflows/release.yml
jobs:
create_pr:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Create PR Let’s add the steps to the job.
First step, we need to checkout the repository.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0Second step, we need to install Node.js.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
name: Install Node.js
with:
node-version: 22 # This is the node version for the create_pr jobThird step, we need to install pnpm.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Install pnpm
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3
id: pnpm-install
with:
run_install: falseFourth step, we need to get the pnpm store directory. This is used to cache the pnpm store directory.
You can skip this step if you are not using pnpm.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Get pnpm store directory
id: pnpm-cache
run: |
echo "pnpm_cache_dir=$(pnpm store path)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUTFifth step, we need to cache the pnpm store directory. This is used to cache the pnpm store directory.
You can skip this step if you are not using pnpm.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- uses: actions/cache@v4
name: Setup pnpm cache
with:
path: ${{ steps.pnpm-cache.outputs.pnpm_cache_dir }}
key: ${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-Sixth step, we need to install the dependencies.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Install dependencies
run: pnpm installBefore we add final create version PR step, we need to create a changeset-version.js file. This file will be used to get the version of the package.
The npx changeset version try to look up for major, minor and patch changes and bump the project’s version accordingly.
In order for changeset to to do this, we need to run pnpm changeset to create a new changeset or version bump. For more information, please refer to this guide Adding a changeset↗.
It will ask you to select an appropriate bump type for the changes made and provide the changelog for the changeset.
After this, a new changeset will be added which is a markdown file with YAML front matter.
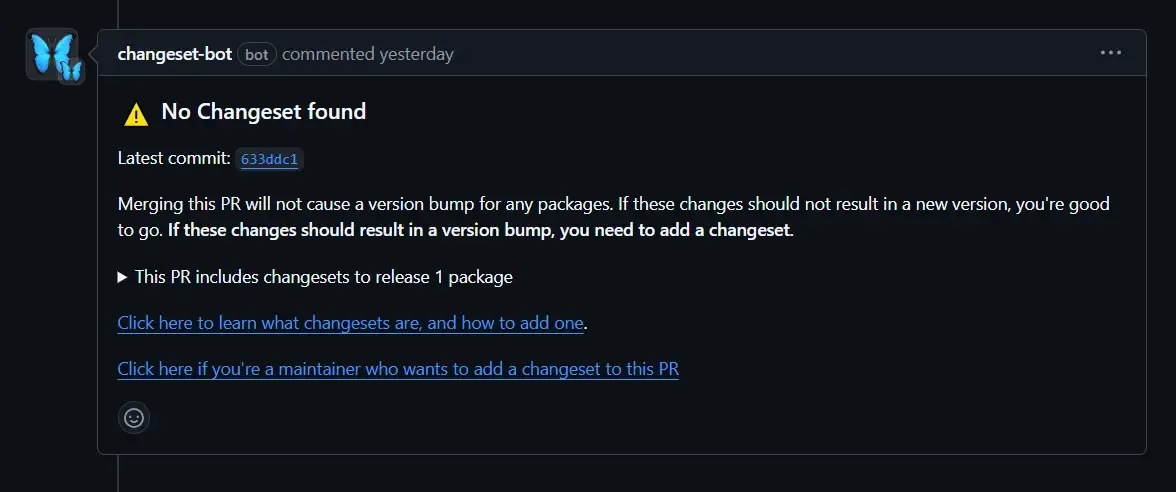
To detect the changeset on the pull request you can setup the changeset bot on your repository which will comment on the pull request with the changeset status.
.github/changeset-version.js
import { exec } from "child_process";
// This script is used by the `release.yml` workflow to update the version of the packages being released.
// The standard step is only to run `changeset version` but this does not update the package-lock.json file.
// So we also run `npm install`, which does this update.
// This is a workaround until this is handled automatically by `changeset version`.
// See https://github.com/changesets/changesets/issues/421.
exec("npx changeset version");
exec("npm install");Next, we need to create the version PR. We need to use the changesets/action action to create the PR. For more information, please refer to the Changesets Release Action↗.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Create Version PR
id: changesets
uses: changesets/action@v1
with:
setupGitUser: true
commit: "chore(release): version packages" # This is the commit message
title: "chore(release): version packages" # This is the title of the PR
version: node .github/changeset-version.js # This is the version of the package
env:
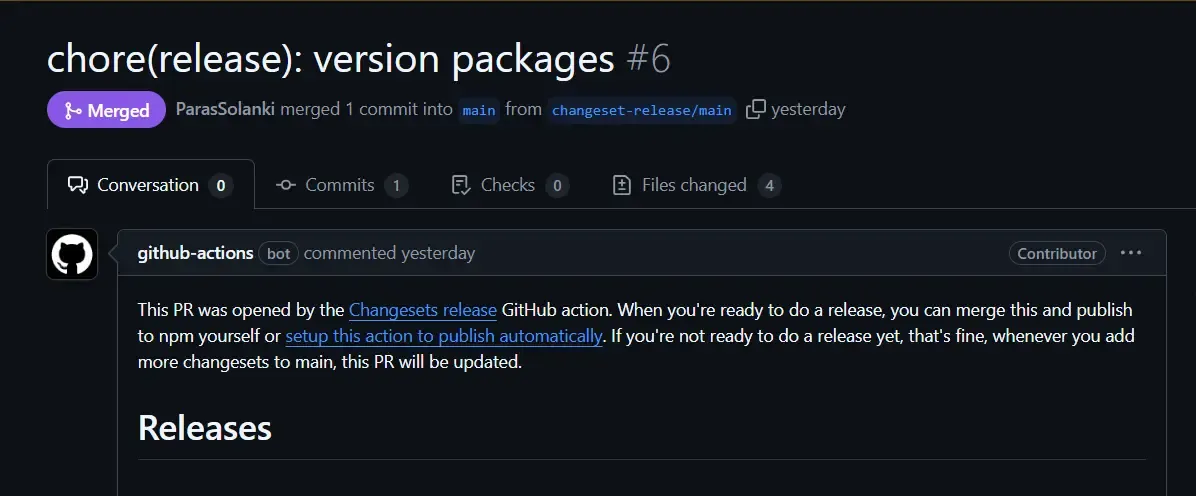
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}So, now when you push to the main branch, it will create a PR with the changeset version.
To publish the package to NPM, we need to add another job called release which will run when the generated PR is merged and has changesets.
We need to add the following steps to the release job. This job needs to run only when the create_pr job has changesets.
.github/workflows/release.yml
jobs:
release:
name: Release
needs: create_pr
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: needs.create_pr.outputs.hasChangesets == 'false'Most of the steps are the same, but we need to add a step to create the .npmrc file.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Creating .npmrc
run: |
cat << EOF > "$HOME/.npmrc"
//registry.npmjs.org/:_authToken=$NPM_TOKEN
EOFNext, add a step to run the build.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Run build
run: pnpm build # This is the build command for your project
env:
NODE_ENV: "production" # Add any environment variables you needNext, add a step to publish the package to NPM. We will use the release script we created in the previous steps.
.github/workflows/release.yml
- name: Publish to NPM
id: changesets
uses: changesets/action@v1
with:
publish: pnpm release:publish # This is the publish command for your project
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_ACCESS_TOKEN }}
NODE_ENV: "production"Once this step is ran for the second time, a new Release will be added to repository. The name of this release will be the new bumped version, and the description will contain all changes added by the contributors**.**

Complete release.yml file:
.github/workflows/release.yml
name: Release
on:
push:
branches:
- main
# cancel previous runs if a new one is triggered
concurrency:
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.event.number || github.ref }}
cancel-in-progress: true
jobs:
create_pr:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Create PR
outputs:
hasChangesets: ${{ steps.changesets.outputs.hasChangesets }}
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Install Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 22 # This is the node version for the create_pr job
- name: Install pnpm
uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3
id: pnpm-install
with:
run_install: false
- name: Get pnpm store directory
id: pnpm-cache
run: |
echo "pnpm_cache_dir=$(pnpm store path)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Setup pnpm cache
uses: actions/cache@v4
with:
path: ${{ steps.pnpm-cache.outputs.pnpm_cache_dir }}
key: ${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-
- name: Install dependencies
run: pnpm install
- name: Create Version PR
id: changesets
uses: changesets/action@v1
with:
setupGitUser: true
commit: "chore(release): version packages"
title: "chore(release): version packages"
version: node .github/changeset-version.js
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
release:
needs: create_pr
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Release Package to npm
if: needs.create_pr.outputs.hasChangesets == 'false'
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Install Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 22 # This is the node version for the release job
- uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3
name: Install pnpm
id: pnpm-install
with:
run_install: false
- name: Get pnpm store directory
id: pnpm-cache
run: |
echo "pnpm_cache_dir=$(pnpm store path)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Setup pnpm cache
uses: actions/cache@v4
with:
path: ${{ steps.pnpm-cache.outputs.pnpm_cache_dir }}
key: ${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-${{ hashFiles('**/pnpm-lock.yaml') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-pnpm-store-
- name: Install dependencies
run: pnpm install
- name: Creating .npmrc
run: |
cat << EOF > "$HOME/.npmrc"
//registry.npmjs.org/:_authToken=$NPM_TOKEN
EOF
env:
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_ACCESS_TOKEN }}
- name: Run build
run: pnpm build
env:
NODE_ENV: "production"
- name: Publish to NPM
id: changesets
uses: changesets/action@v1
with:
publish: pnpm release:publish
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
NPM_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NPM_ACCESS_TOKEN }}
NODE_ENV: "production"Conclusion
This is a basic guide on how to automate the changeset releases. You can extend this guide to your needs.
Thank you for reading this and I hope you liked it!